Living with diabetes requires constant vigilance and monitoring of blood glucose levels to ensure optimal health outcomes. Regular blood sugar testing plays a crucial role in managing diabetes effectively and preventing complications associated with fluctuating glucose levels.
Why is Monitoring Blood Sugar Important for Diabetics?
Understanding blood glucose levels is essential for individuals with diabetes as it allows them to track how their bodies respond to various factors such as food, exercise, and medications. Blood sugar regulation is important to maintaining overall well-being and reducing the risk of long-term complications.
High blood sugar, also known as hyperglycemia, can have detrimental effects on the body, leading to symptoms such as increased thirst, frequent urination, and fatigue. It can also contribute to serious complications like nerve damage, kidney disease, and cardiovascular issues.
Conversely, managing low blood sugar levels, known as hypoglycemia, is equally important to prevent emergencies like seizures or loss of consciousness. Diabetics must strike a balance and keep their blood glucose within a healthy range.
How to Properly Use a Blood Glucose Meter for Testing
Setting up your glucose meter involves following the manufacturer’s instructions to ensure accurate results. This includes inserting fresh batteries, calibrating the device if necessary, and ensuring the test strips are within their expiration date.
Using test strips for accurate results requires proper technique such as obtaining a sufficient drop of blood for testing and applying it correctly to the strip. Consistent and correct usage of the test strips ensures reliable readings for effective diabetes management.
Interpreting glucose meter readings involves understanding the numbers displayed by the meter and taking appropriate action based on the results. Trends in blood glucose levels over time can provide valuable insights for adjusting diet, medication, and lifestyle choices.
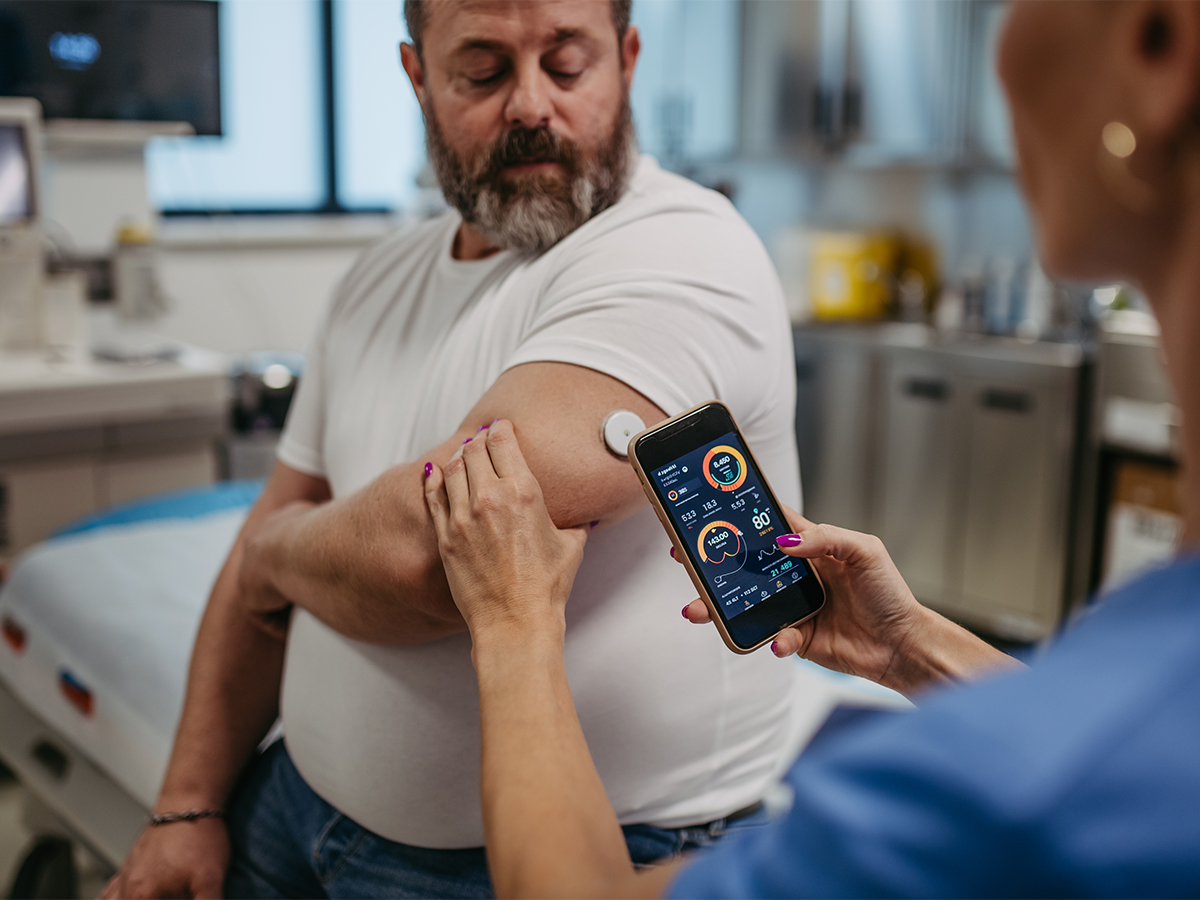
Benefits of Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Blood Glucose Management
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) offers a more comprehensive approach to blood sugar monitoring compared to traditional periodic testing. It provides real-time data on glucose levels, helping individuals make immediate adjustments to optimize their diabetes management.
Adjusting treatment plans based on data obtained from CGM empowers individuals and healthcare providers to tailor interventions according to individual needs. This personalized approach leads to better control of levels and reduces the risk of complications.
Improving blood sugar regulation with CGM can enhance the quality of life for people with diabetes by promoting proactive management and early intervention. Continuous monitoring allows for proactive identification of trends and patterns, enabling timely adjustments to prevent hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia.
Best Practices for Checking Your Blood Glucose Levels Regularly
Establishing a schedule for routine testing ensures consistency and helps individuals stay on track with their diabetes management. Regular monitoring is key to detecting changes in glucose levels and adjusting treatment plans accordingly.
Tips for using your blood glucose meter correctly include storing it properly, keeping test strips in a dry place, and cleaning the device regularly to maintain accuracy. Proper maintenance and usage of the meter contribute to reliable and effective monitoring.
Seeking help from healthcare providers when needed is important for addressing any concerns or issues. Healthcare professionals can offer guidance, support, and adjustments to treatment plans based on individual circumstances and needs.
Understanding the Role of Blood Sugar Monitoring in Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes
Differentiating between blood glucose management for Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes is essential due to the distinct characteristics and treatment strategies for each condition. Individuals with Type 1 diabetes often require insulin therapy, while those with Type 2 diabetes may manage their condition through diet, exercise, and medication.
Challenges Faced in Monitoring Blood Sugar
Levels may vary between Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes, influenced by factors such as insulin sensitivity, lifestyle choices, and individual health status. Understanding these challenges helps individuals and healthcare providers develop tailored monitoring plans.
Benefits of personalized blood sugar monitoring plans include improved glycemic control, reduced risk of complications, and enhanced quality of life. By customizing monitoring strategies to individual needs and preferences, individuals can better manage their diabetes and achieve optimal health outcomes.
Simplify Your Diabetes Management with Medically Modern
Tired of the endless cycle of finger pricking to check your blood sugar? Medically Modern is here to change the game for insulin-dependent diabetics. We specialize in helping you gain access to Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGM) through your doctor, supported by Medicare, to make managing your diabetes simpler and virtually pain-free.
With CGM, you can say goodbye to the traditional, painful methods of monitoring your glucose levels and welcome a new era of diabetes care. These advanced devices provide real-time insights into your blood sugar, allowing for better control and a deeper understanding of how your lifestyle affects your diabetes.
Don’t let finger pricking hold you back from living your life to the fullest. Let Medically Modern help you transition to a CGM, ensuring you can manage your diabetes more effectively without the constant discomfort. Get in touch with us today, and take the first step towards a less invasive, more informed way of controlling your diabetes.
Checking your levels regularly with a blood glucose meter allows diabetics to monitor their blood glucose levels and make informed decisions about their diet, medication, and lifestyle choices.
A blood glucose meter is a device used to measure the amount of glucose in a small sample of blood. Diabetics use a blood glucose meter to monitor their blood sugar levels throughout the day.
To use a meter, you typically prick your finger to obtain a small blood sample, apply it to a test strip, and then insert the strip into the meter to get a reading of your blood glucose levels.
Symptoms, also known as hypoglycemia, include sweating, shakiness, dizziness, hunger, confusion, and in severe cases, loss of consciousness. Diabetics need to be aware of these symptoms and take appropriate action when they occur.
The frequency of blood glucose testing may vary depending on the type of diabetes, your treatment plan, and your doctor’s recommendations. Typically, diabetics are advised to test their blood sugar multiple times a day, especially before meals and at bedtime.
Monitoring your blood sugar levels allows you to track how your body responds to food, exercise, and medication. It helps you make adjustments to your diabetes management plan to keep your blood glucose levels within the target range.
Proper use of glucose meters and test strips is essential for accurate results. Factors such as expired test strips, improper storage of test strips, and inadequate blood sample size can impact the reliability of your readings.